Function Of Dna Ligase Enzyme | Coli is a polypeptide of molecular weight 75,000. Often involve putting genes · into viruses or bacteria using a vector. This happens because dna polymerases can only read the dna template from the 5' to the 3' end and add free. Jump to navigationjump to search. Dna ligase — dna li·gase (liґgās) an enzyme of the ligase class that catalyzes the energy driven linkage of a double stranded dna chain with a free 3′ hydroxyl group to one with a 5′ phosphate group, forming a phosphodiester bond between them … medical dictionary.
You do not need to be a curator in order to contribute. Dna replication enzymes include the dna polymerase, dna helicase, dna ligase, dna topoisomerase enzymes needed for the dna replication process in eukaryotes and in prokaryotes. Dna ligase or polynucleotide ligase catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester linkage between two immediate neighbour nucleotides of a dna strand. Dna ligase is an enzyme required for joining the two dna ends by creating phosphodiester bonds between them. Which dna ligase is used frequently in the ampligase dna ligase, isolated from the thermophilic bacteria and can actively work at 95°c.
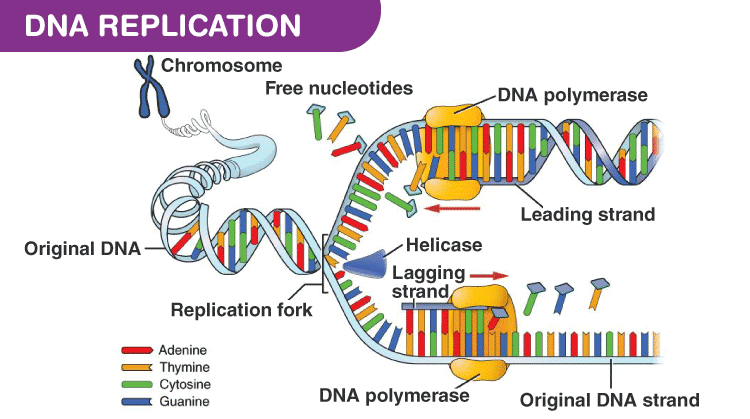
Furthermore, mammals have four subtypes of ligases that vary in their function; In molecular biology, dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. Instead, another enzyme, dna ligase, seals off the nicks by using high energy phosphodiester bonds in atp or nad to join a free 3′ hydroxyl with an adjacent 5′. Dna ligase (polydeoxyribonucleotide synthase) is the enzyme that joins two single stranded dna fragments by catalyzing the formation of an many dna ligases are identified from different sources, which have their own specific characters, molecular weights, requirements and mode of functions. The enzyme has been applied in dna sequencing methods in diverse ways, by taking advantage of the fact that dna ligase does not require dntps as substrates for its function, since. Basic scheme of ligation of two dna molecules. Coli, dna functions as helicase; Coli) is the 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity. In molecular biology it is commonly used for. This happens because dna polymerases can only read the dna template from the 5' to the 3' end and add free. Coli is a polypeptide of molecular weight 75,000. Dna ligase (ec 6.5.1.1) is the enzyme at the heart of the dna ligation reaction. This is the currently selected item.
You do not need to be a curator in order to contribute. This protein is a hexamer and it moves with the replication fork. The main function of exonucleases like dna polymerase i is to remove the rna primer segments from the template strand. Restriction enzymes & dna ligase. The dna ligase catalyzes the formation of covalent phosphodiester linkages, which permanently join the nucleotides together.
It seals repairs in the dna, it seals recombination fragments, and it connects okazaki fragments (small dna fragments formed during the replication of. This is the currently selected item. Dna ligase 1provided by hgnc. Dna ligase is an enzyme required for joining the two dna ends by creating phosphodiester bonds between them. While helicase works to unwind the dna molecule, ligase is the replication enzyme that binds the fragments together by addition of phosphates in the gaps that. Anyone should feel free to add themselves as a curator for this consensus protocol. Dna ligase — dna li·gase (liґgās) an enzyme of the ligase class that catalyzes the energy driven linkage of a double stranded dna chain with a free 3′ hydroxyl group to one with a 5′ phosphate group, forming a phosphodiester bond between them … medical dictionary. In molecular biology, dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. You can think of a dna strand as one long charm bracelet with four different types of charms. In this situation we need to discuss about dna and its structure. This happens because dna polymerases can only read the dna template from the 5' to the 3' end and add free. You do not need to be a curator in order to contribute. The charms just hang off the strong chain the dna ligase enzyme detects places where the sugar and phosphate chain is broken, and rebuilds the link, connecting the sugar and phosphate.
It has three general functions: In molecular biology, dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. Usually, scientists select two different enzymes for adding an insert into a vector (one enzyme on the 5' end and a different enzyme on the 3' end). You can think of a dna strand as one long charm bracelet with four different types of charms. Dna ligase 1provided by hgnc.

Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and lagging strand describe the process of dna replication and the functions of the enzymes involved Dna ligases represent a fundamental class of enzymes required by all organisms to maintain the. Anyone should feel free to add themselves as a curator for this consensus protocol. This is the currently selected item. Dna ligase — dna li·gase (liґgās) an enzyme of the ligase class that catalyzes the energy driven linkage of a double stranded dna chain with a free 3′ hydroxyl group to one with a 5′ phosphate group, forming a phosphodiester bond between them … medical dictionary. Basic scheme of ligation of two dna molecules. Instead, another enzyme, dna ligase, seals off the nicks by using high energy phosphodiester bonds in atp or nad to join a free 3′ hydroxyl with an adjacent 5′. This happens because dna polymerases can only read the dna template from the 5' to the 3' end and add free. Message subject (your name) has forwarded a page to you from science. It has three general functions: Dna ligase (ec 6.5.1.1) is the enzyme at the heart of the dna ligation reaction. Usually, scientists select two different enzymes for adding an insert into a vector (one enzyme on the 5' end and a different enzyme on the 3' end). What are the 3 things listed about dna ligase function?
Dna ligase (polydeoxyribonucleotide synthase) is the enzyme that joins two single stranded dna fragments by catalyzing the formation of an many dna ligases are identified from different sources, which have their own specific characters, molecular weights, requirements and mode of functions ligase enzyme function. The process of ligase enzyme for joining the two ends of dna strands is called ligation.
Function Of Dna Ligase Enzyme: What are the 3 things listed about dna ligase function?
Posting Komentar